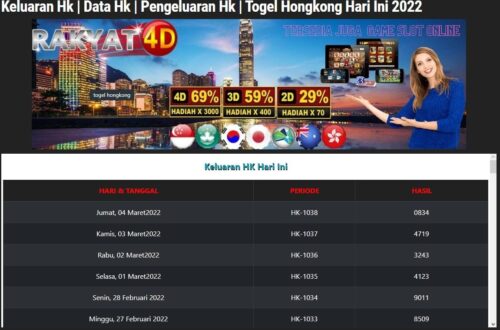
Lottery is an activity where people pay money in exchange for the chance to win a prize. The prize is normally a large amount of cash. While many people enjoy playing the lottery for entertainment, others use it as a way to improve their lives financially. However, the odds of winning are low, so it is important to understand how the game works before you play.
There are many ways to participate in a lottery, including joining a pool and buying tickets. A pool can be comprised of coworkers or friends, and each person contributes a small sum of money to the group. The manager of the pool then buys lottery tickets on behalf of the group. The pool can be as large as 50 members, and if the lottery wins, each member will receive a share of the prize value.
In addition to buying lottery tickets, people can also enter raffles, which are a type of lottery. The prizes in these lotteries can be money, goods, or services. The chances of winning are based on the number of tickets sold. Many states have regulations governing the operation of lotteries. The regulations may include minimum age requirements, minimum ticket purchase amounts, and other restrictions. The purpose of these rules is to protect the interests of participants and the public.
Generally, the larger the jackpot, the more tickets are sold. This can increase the chances of someone winning and the overall size of the prize pool. However, if the odds of winning are too low, ticket sales will decline. Lotteries should strike a balance between the size of the prize pool and the number of tickets sold.
Another way to increase your chances of winning is to pick numbers that are less common. Using the number seven or your children’s birthdays is one way to do this. But Glickman warns that this strategy can backfire if other players also pick those same numbers. He advises that you try to choose numbers that are not in the same group, such as 1, 3, and 5. The more different numbers you have, the more combinations there will be, and your odds of winning will be higher.
Lotteries are used to raise funds for a variety of purposes, from municipal infrastructure projects to disaster relief. They are an effective fundraising tool because they are easy to organize and popular with the general public. In addition, they are less expensive than other forms of fundraising. However, they have been criticized for being addictive and can cause people to lose track of other financial obligations.
The first European lotteries appeared in the 15th century with towns attempting to raise funds for fortifications or to aid the poor. They became more widespread in the 16th century with Francis I of France permitting the establishment of public lotteries. By the 18th century, they were widely established and largely funded by taxes. Lotteries remain popular in Europe today, with more than 100 national and regional lotteries in operation.